SMB
Enabling Samba/SMB in the cluster
Note
Before enabling SMB please ensure all relevant Samba packages (i.e. Samba, NMB, Winbind) are installed and enabled on all nodes in the cluster.
By default RSF-1 does not manage SMB shares - the smb.conf file is
left to be managed by the system administrator manually on each node in the cluster.
To enable the management of the SMB from the webapp and
synchronise it across all cluster nodes, navigate to
Shares -> SMB and click ENABLE SMB SHARE HANDLING:

You will now be presented with the main SMB shares screen consisting of a number of tabs to handle different aspects of SMB configuration.
Initial SMB configuration
SMB/Samba provides numerous ways to configure authentication and sharing depending upon the environment and the complexity required. This guide documents two commonly used configurations:
- User Authentication - standalone clustered SMB sharing with local user authentication.
- ADS Authentication - member of an Active Directory domain with authentication managed by a domain controller.
Local User Authentication
With local user authentication, cluster users must be created with the SMB support enabled. A user created this way will have the same login name, UID and GID on all nodes in the cluster along with an equivalent Samba user entry to provide the required SMB authentication. See Unix users in this guide for further details.
Configuring Samba Globals for User Authentication
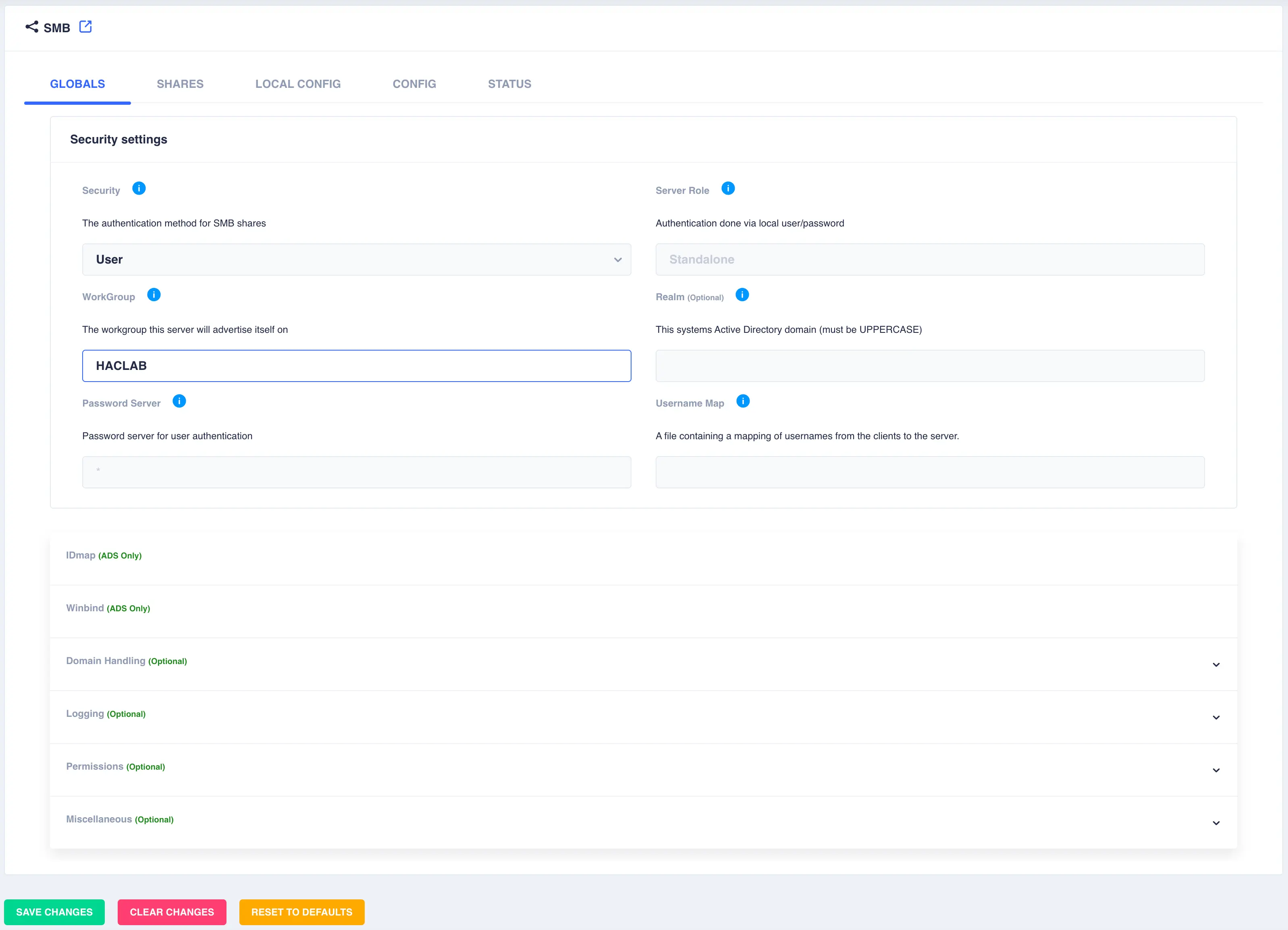
Navigate to Shares -> SMB, select the GLOBALS tab, then select User from the drop down security
list and optionally set the desired workgroup name. Click save changes:
ADS Authentication
RSF-1 can also be configured to use Active Directory for user authentication (ADS) when being deployed for use in a Microsoft environment.
In a Microsoft environment users are identified using security identifiers (SIDs). A SID is not just a number, it has a structure and
is composed of several values, whereas Unix user and group identifiers consist of just a single number. Therefore a mechanism needs to be
chosen to map SIDs to Unix identifiers. Winbind (part of the Samba suite) is capable of performing that mapping using a number of such
mechanisms known as Identity Mapping Backends; two of the most commonly used being tdb (Trivial Data Base) and rid (Relative IDentifier).
tdb - The default idmap backend is not advised for an RSF-1 cluster as tdb generates and stores UIDs/GIDs locally on each cluster node,
and works on a "first come first served" basis. When allocating UIDs/GIDs it simply uses the next available number with no consideration
given to a clustered environment, which can lead to UID/GID mismatches between cluster nodes.
rid - This mechanism is recommended as the idmap backend for a clustered environment. rid implements a read-only API to retrieve account and group information
from an Active Directory (AD) Domain Controller (DC) or NT4 primary domain controller (PDC). Therefore using this approach ensures UID/GID continuity on all cluster nodes.
When using the rid backend, a windows SID (for example S-1-5-21-1636233473-1910532501-651140701-1105) is mapped to a UNIX UID/GID by
taking the relative identifier part of the SID (the last set of digits - 1105 in the above example) and combining it with a preallocated range of numbers to provide
a unique identifier that can be used for the UNIX UID/GID. This preallocated range is configured using the Samba IDMAP entry.
Configuring Samba Globals for ADS Authentication
-
Navigate to
Shares -> SMB, select theGLOBALStab, then selectADSfrom the drop down security list, set the workgroup and realm name. Clicksave changes: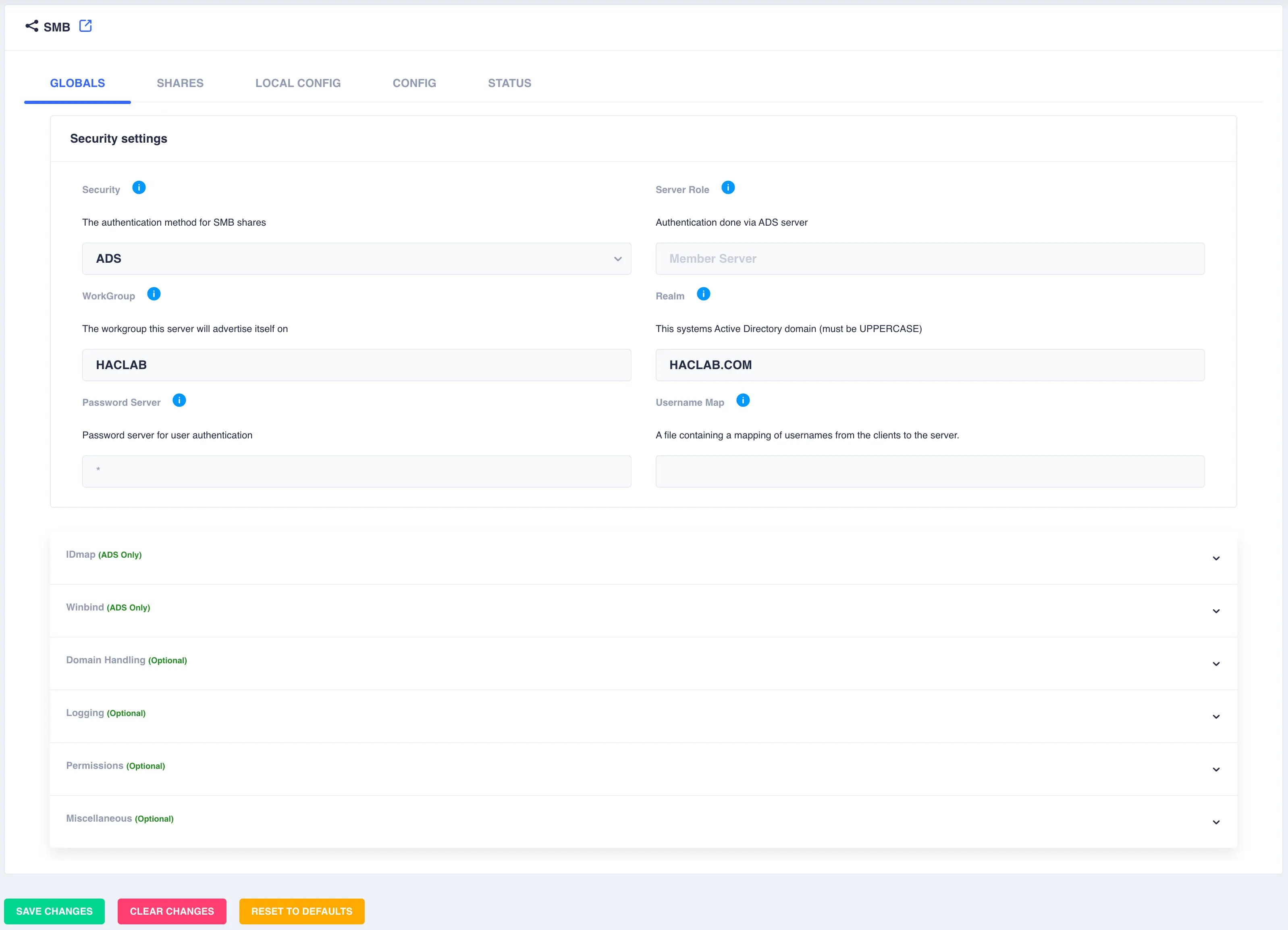
-
Navigate and open the
IDMAPsetting section. By default a wildcard entry is preconfigured (this is used by Samba as a catchall and is a required entry). Click+Addand configure an entry for theridmapping. Enter the same workgroup name used in the security settings and enter the desired range of numbers to use for mapping the IDs. Select a range that starts after the wildcard range and provide enough scope to cover the expected maximum number of windows users in the domain. Click the✓to update the mapping table: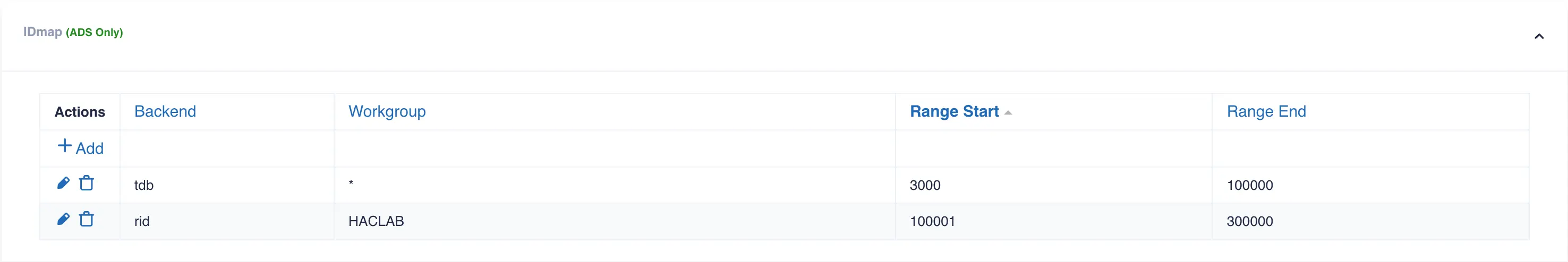
-
Click
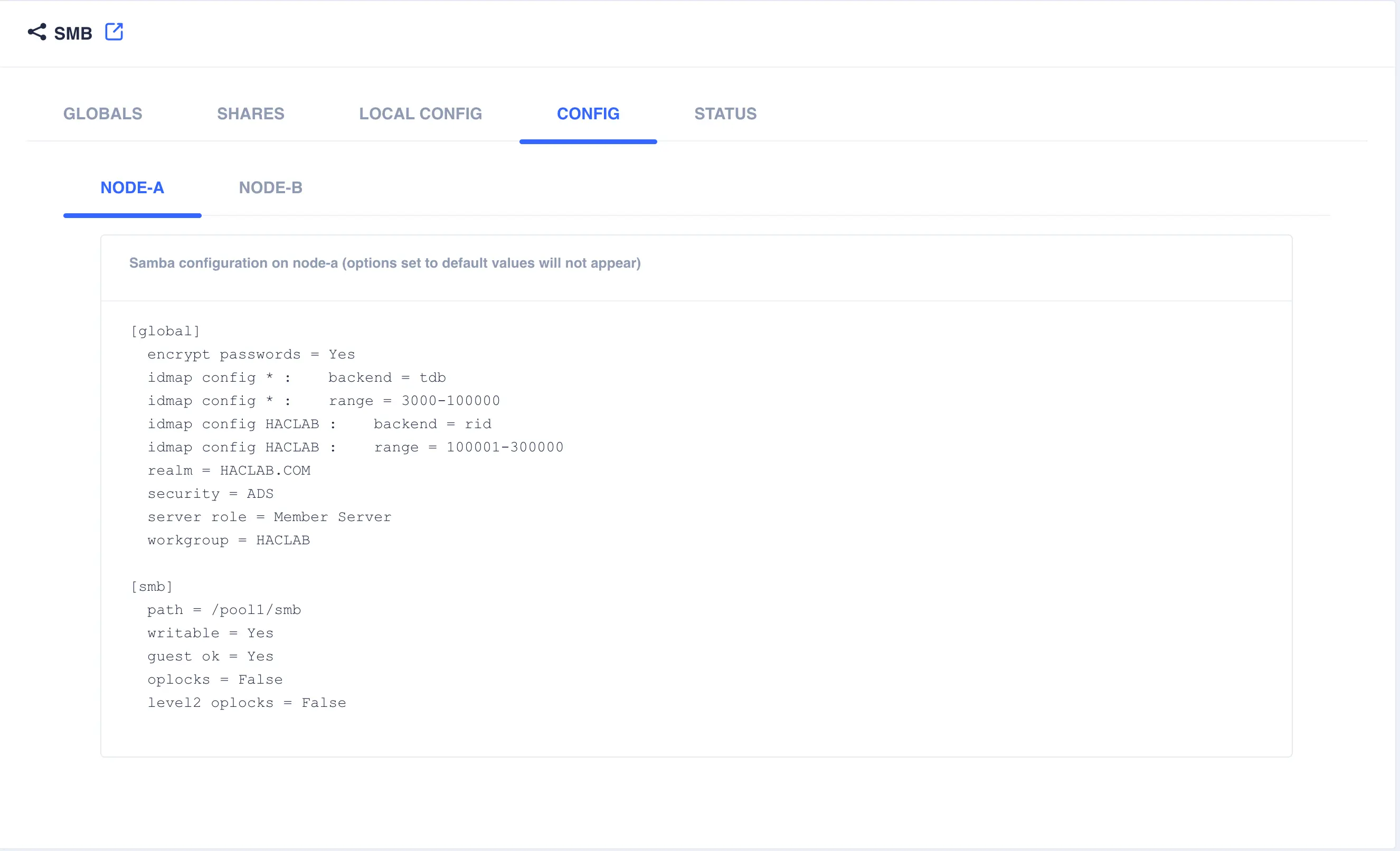
SAVE CHANGES. The resulting configuration file (viewable from theCONFIGtab) should look similar to the following:[global] encrypt passwords = Yes idmap config * : backend = tdb idmap config * : range = 3000-100000 idmap config HACLAB : backend = rid idmap config HACLAB : range = 100001-300000 realm = HACLAB.COM security = ADS server role = Member Server workgroup = HACLAB
Samba is now configured to be able use ADS authentication.
Testing ADS authentication (optional)
ADS authentication can be tested by allowing users from the windows domain to login to the Unix cluster hosts. A successful login proves that Samba is able to authenticate using the Windows Domain Controller.
Some additional configuration is required as follows (remember to do this on all nodes in the cluster):
-
Configure winbind authentication for users and groups in the name service switch file
/etc/nsswitch.conf. Addwinbindas a resolver for users and groups:This tells the operating system to lookup users locally first (passwd: files winbind systemd group: files winbind systemd/etc/passwd), followed bywinbind. -
Change DNS in
/etc/resolv.confso it refers to the Active Directory server:domain haclab.com search haclab.com nameserver 10.254.254.111 -
Join the active directory domain.
# net ads join -U Administrator Password for [HACLAB\Administrator]: Using short domain name -- HACLAB Joined 'WCALMA1' to dns domain 'haclab.com' No DNS domain configured for wcalma1. Unable to perform DNS Update. DNS update failed: NT_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER # net ads info LDAP server: 10.254.254.111 LDAP server name: ws2022.haclab.com Realm: HACLAB.COM Bind Path: dc=HACLAB,dc=COM LDAP port: 389 Server time: Fri, 13 Sep 2024 17:07:32 BST KDC server: 10.254.254.111 Server time offset: 1 Last machine account password change: Fri, 13 Sep 2024 16:57:04 BST -
Restart
winbind.# systemctl restart winbind -
Query
winbindto confirm it is able to query the Active Directory server:# wbinfo -U HACLAB\administrator HACLAB\guest HACLAB\krbtgt HACLAB\hacuser1 HACLAB\hacuser2
Samba can be further configured to allow AD users to login if so desired. Two further steps are required:
-
Enable auto creation of home directories. For Debian based systems:
For RedHat based systems:# vi /etc/pam.d/common-session # add to the end if you need (auto create a home directory at initial login) session optional pam_mkhomedir.so skel=/etc/skel umask=077# authselect enable-feature with-mkhomedir # systemctl enable --now oddjobd -
Configure a login shell for Samba. Navigate to
Shares -> SMB, select theGLOBALStab, expand themiscellaneoussection and set an appropriate login shell for the system: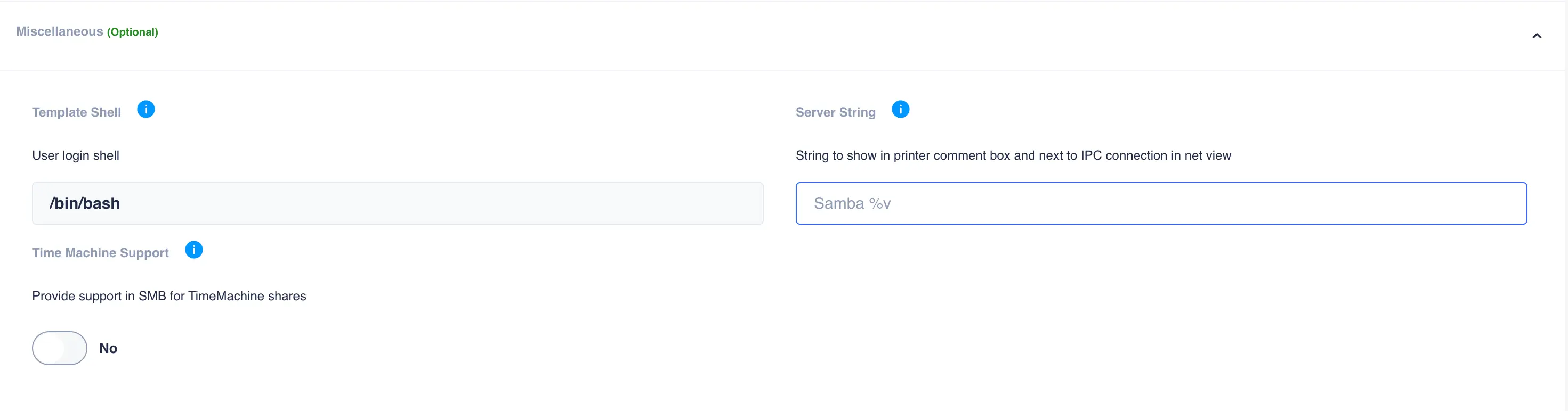
-
Finally, restart
winbind.# systemctl restart winbind
It should now be possible to login to the Unix servers using AD users.
Clustering an SMB Share
These steps show the process of creating a clustered SMB share.
-
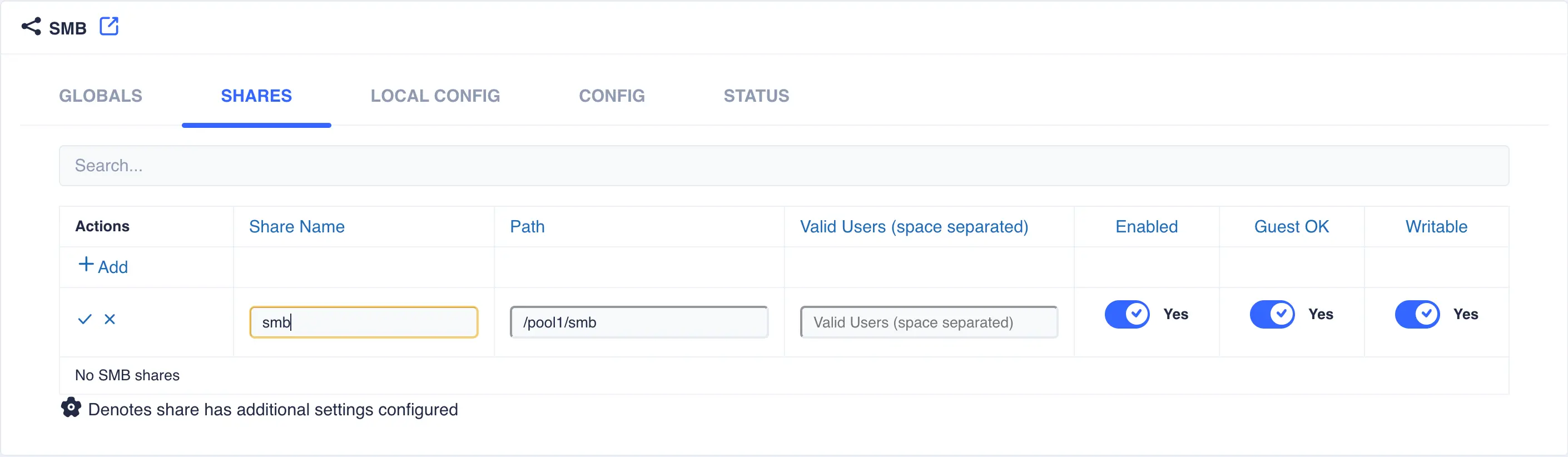
Shares are managed via the
SHAREStab. Click+Addto create a new SMB ShareAvailable options:
Share NameThe name of the SMB sharePathPath of the folder to be shared, for example/pool1/SMBValid UsersA space separated list of Valid users. When User authentication is in effect these will be Unix Cluster users; for ADS authentication this can be local Unix cluster and Windows domain users.
-
Click
✓when done. The share will now be available and clustered (a Samba reload is automatically applied):
-
Advanced share settings can be applied once the share is created by clicking the cog on the left hand side of each individual share:
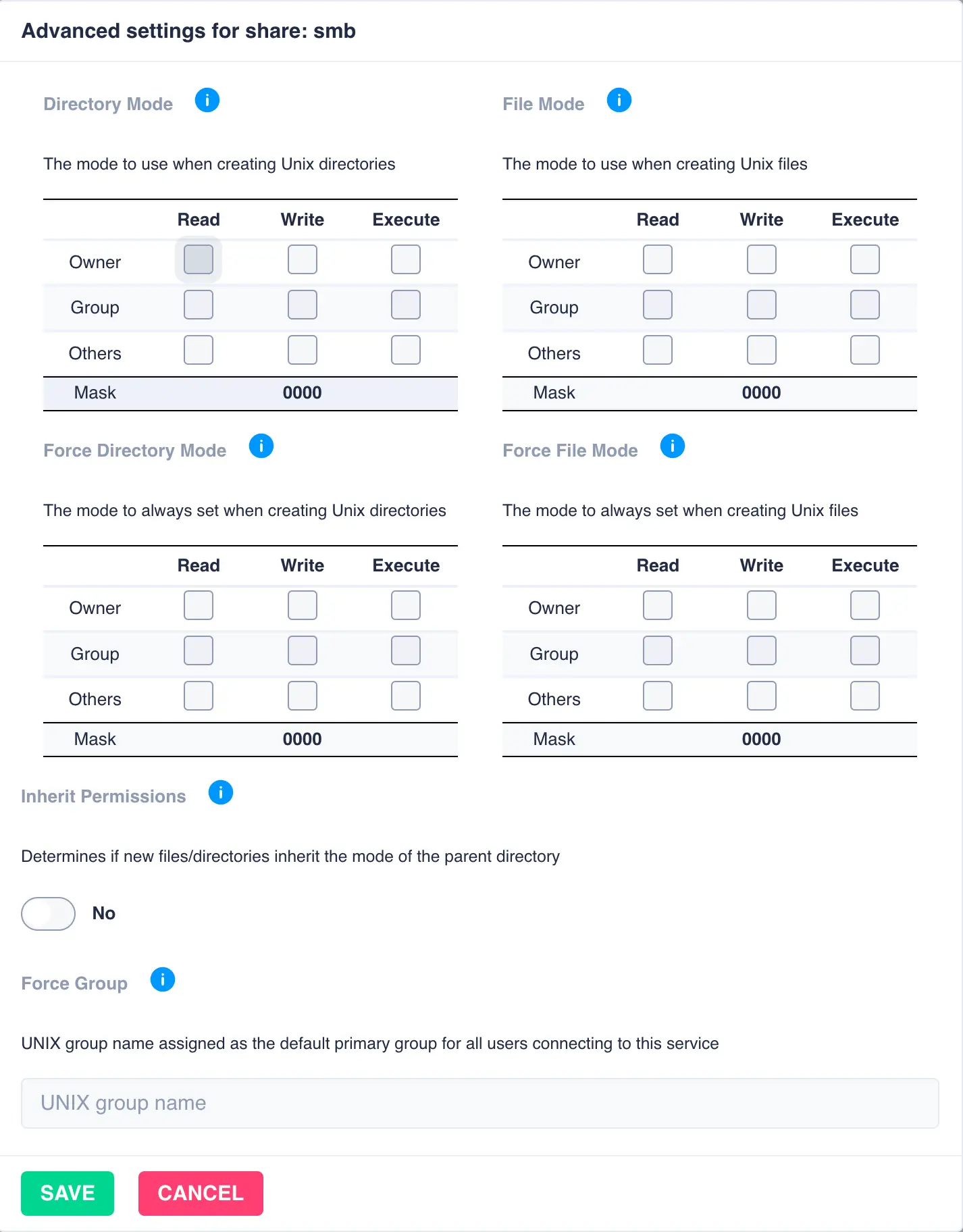
Additional SMB settings
LOCAL CONFIG
This tab is used to apply Samba configuration settings specific to each node rather than all cluster nodes. One example
of this is the netbios name which needs to be unique on each node in the Windows Domain.
CONFIG
The tab shows the current Samba configuration for each cluster node; this view includes the globals, shares and local configuration.
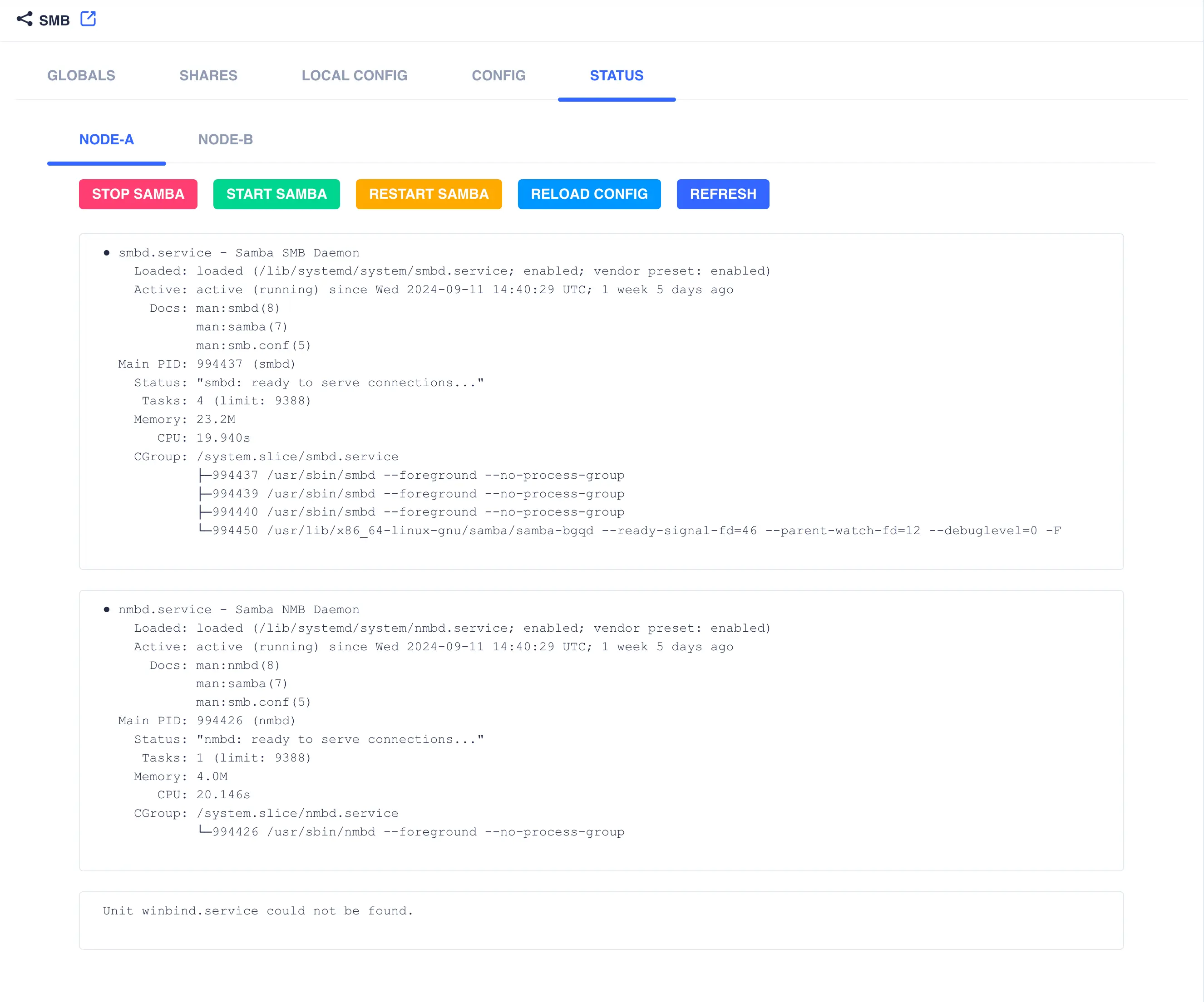
STATUS
This tab shows the status of the Samba daemon services that are running. It also allows management of the services per node.